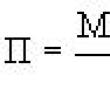Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Chef's job description: duties, requirements and rights
- Job description of a loader driver
- Holidays doubly everything is paid Who can be attracted to work on weekends and holidays
- Designer categories Engineer category 1 category
- Beauty salon executive director employment contract
- Is an injury on the way to work considered a production injury?
- Cleaner of production and service premises
- Personal leave with the police
- Pathologist
- Job descriptions of a psychologist in an organization
Advertising
| General concepts of marketing. Marketing |
What is Marketing? Many people think that marketing is all about sales. Not surprisingly, we are bombarded with hundreds of commercials, newspaper ads and sales announcements every day. However, advertising and sales are nothing more than an integral part of marketing. They exist as two integral components of marketing. Marketing is the process of predicting the needs of potential buyers and meeting these needs by offering appropriate products - products, technologies, services, etc. TO main types of marketing activities relate:
Marketing goalThe goal of modern marketing is not a sale or by any means (including cheating the buyer), but. Marketing goal- attract new customers, promising them the highest, and retain old customers, constantly satisfying their changing. The main task of marketing- understand the needs and requirements of each market and select those that their company can serve better than others. This will enable the company to produce higher quality products and thereby increase sales and increase its revenues by better meeting the needs of its target customers. Marketing begins long before a company has a finished product. Marketing begins with the fact that managers identify people, calculate their intensity and volume, and determine the company's ability to satisfy them. Marketers continue to work on products throughout its entire life cycle. They try to find new customers and retain existing ones by improving the consumer properties of the product and using sales reports and feedback for this purpose. If a marketing specialist has done a good job - he correctly understood the needs of the client, created a product that meets the requirements of buyers, set a reasonable price, correctly distributed the product and conducted an advertising campaign, then it will be very easy to sell such a product. Marketing Is a social and managerial process by which individuals and groups of people meet their needs and wants through the creation and exchange of goods with consumer value. To explain this definition, it is necessary to consider several concepts directly related to marketing:
Marketing principlesIn modern economic practice, the relationship of the organization with the majority of market entities should be based on the principles of marketing. Basic principles of marketing:
Thus, marketing should be viewed as an economic, social, managerial and technological process based on the following basic principles:
Managing the behavior of an organization based on marketing principles should ensure that it operates in a dynamic, continuous (ring) mode that provides flexibility and adaptability of the organization to turbulent changes in the market environment. The goal of managing the behavior of an organization based on marketing principles is to determine the promising directions of the organization's activities in the market, which provide the organization's competitive advantages with minimal resource costs. The main objectives of marketing:
Functions and types of marketingThe main functions of marketing:
Types of marketingDepending on the scope and object of application, the following types of marketing are distinguished:
Conditions of demand and marketing challengesDemand can be: negative, absent, hidden, falling, irregular, full-fledged, excessive, irrational. Negative demand caused by the negative attitude of buyers towards the product or service. The challenge for marketing under these conditions is to analyze why the market is hostile to the product, and whether the marketing program can change the negative attitude to the product by redesigning it, lowering prices, and more active incentives. Lack of demand... Target consumers may not be interested in the product or are indifferent to it. The challenge for marketing is to find ways to align the inherent benefits of a product with the natural needs and interests of a person. Hidden demand- this is when many consumers cannot satisfy their desires with the help of goods and services offered on the market (harmless cigarettes, more economical cars). Marketing's task is to assess the size of the potential market and create effective products and services that can meet demand. Falling demand... The task of marketing is to analyze the reasons for the decline in demand and determine whether it is possible to stimulate sales again by finding new target markets, changing the characteristics of the product, etc. Irregular demand(fluctuations on a seasonal, daily and even hourly basis): - rush hours for transport, overloading museums on weekends. The challenge for marketing is to find ways to smooth out fluctuations in the distribution of demand over time through flexible prices, incentives, and other incentives. Full demand... Such demand usually occurs when the organization is satisfied with its turnover. The challenge for marketing is to maintain the current level of demand, despite changing consumer preferences and increasing competition. Excessive demand- this is when the level of demand is higher than the ability to satisfy it. The task of marketing, referred to in this case as "demarketing", is to find ways to temporarily or permanently reduce demand, not eliminate it. Irrational demand, i.e. demand for unhealthy goods and services; cigarettes, alcoholic beverages, drugs, etc. Marketing's job is to convince these hobbyists to give up such habits. Marketing as a market management conceptAll companies want to be successful. Many factors are important for a company's prosperity: the right strategy, dedicated employees, a well-established communication system, and accurate implementation of the marketing program. However, today's successful companies at all levels have one thing in common - they focused on the consumer as much as possible and all work is built on the basis of marketing. All of these companies are dedicated to one goal: understanding and meeting customer needs in clearly defined target markets. They motivate every employee in their company to create the highest customer value while ensuring complete customer satisfaction. They know that only this approach will allow them to obtain the desired market share and profit. Yet it is the marketing departments that care more about consumers than other departments. Customer creation and satisfaction are at the heart of today's marketing theory and practice. Some believe that only the work of large companies operating in is based on marketing. Indeed, marketing is critical to the success of any firm, large or small, commercial or non-commercial, national or international. In the business sector, marketing has found its application primarily in companies that produce packaged consumer goods, consumer durables, and industrial goods. In recent decades, service companies, especially airlines, insurance and financial institutions, have also begun to use marketing in their activities. Some professionals in private practice (lawyers, accountants, doctors, architects, etc.) also became interested in marketing and began to use its techniques vigorously. Marketing has become an integral part of the strategies of many non-profit organizations, in particular colleges, hospitals, museums, philharmonics and even churches. Marketing is widely used today in all countries of the world. Most countries in the Americas, Western Europe and Southeast Asia have extensive marketing systems. Even in Eastern Europe and the former Soviet republics, where the very word "marketing" sounded unusual until recently, significant political and social changes created the conditions for the introduction of marketing. Economic and political leaders in most countries of the former socialist camp are eager to learn everything about modern marketing practice. You already know a lot about marketing - it's all around you. You see the marketing results - this is an abundance of products on store shelves. Marketing is advertising that has flooded TV screens, magazines, newspapers, and even reaches your inbox. At home and at school, at work and during leisure, marketing is everywhere, no matter what you do. Marketing is more than an alert buyer. There is a vast network of people behind it, busy fighting for your attention and money. In the manual, you will come across a more complex, scientific definition of the basic concepts and practices of modern marketing. In this chapter, we start by defining marketing and its foundational concepts; find out what philosophy is at the heart of the theory and practice of marketing; Let's discuss some of the main problems that marketing faces in the process of its development. What is MarketingWhat does the term "marketing" mean? The goal of modern marketing is not to sell on a "no-no-no-sell-no-sell" basis, but customer satisfaction. Some people think that marketing is just advertising and selling. Not surprisingly, we are bombarded with hundreds of TV commercials, newspaper ads, sales letters and sales announcements every day. Someone is constantly trying to sell us something. It seems that not only death and taxes are inevitable, but also sales. So it might surprise you if we say that selling and advertising is just the tip of the marketing iceberg. While these two are essential, they are nothing more than building blocks of the marketing mix, and often not the most important. If a marketing specialist has worked hard to understand the needs of the client, created a product that represents the highest consumer value, set a reasonable price, distributed the product correctly and effectively advertised it, then it will be very easy to sell such a product. Everyone has heard of the so-called hot goods. When Sony created its first Walkman player, Nintendo offered the first video game console, and The Body Shop launched its unique cosmetics, and there were a huge number of orders for these products. This is because the companies were able to offer the "right" products. Not just products that many would like to purchase, but products that open up new opportunities. Peter Drucker, one of the leading management theorists, states: "The goal of marketing is to get to know and understand the customer so that the product or service exactly matches his requirements and sells itself." Thus, sales and advertising are only part of a rather complex "marketing mix" - a set of marketing tools that affect the market. We define marketing as a social and managed process by which individuals and groups of people meet their needs and wants through the creation of goods and and them with each other. To explain this definition, we will consider the following concepts:, and; products; customer value, satisfaction and quality; exchange, transactions and relationships; market. MarketsMarket Is a collection of existing and potential buyers of the product. These buyers have common needs or requests that can be met through an exchange. Thus, the size of the market depends on the number of buyers who have a need for a product, have the resources to exchange, and are willing to offer those resources in exchange for the product they want. Fig. Market relationship Initially, the term "market" meant a place where buyers and sellers could make their own (such a place was, for example, the central square of a settlement). Economists use the term "market" to mean the aggregate of buyers and sellers who buy and sell certain types of goods; there is, for example, a real estate market or a grain market. Marketers, however, view sellers as representatives of production and buyers as representatives of the market. The relationship between production is shown in the figure above. There are four streams that connect sellers and buyers: sellers deliver goods, services, and messages to the market; in return, they receive money and information from buyers. The inner loop shows the exchange of money for a commodity; external - information exchange. The modern economy is based on a division of labor, in which each manufacturer specializes in the production of a certain commodity, receives money for this and buys everything necessary for production with it. Consequently, the modern economy consists of many markets. The producer turns to the resource market (raw materials market, labor market, foreign exchange market), acquires resources, turns them into goods and services, sells them to an intermediary, and he sells them to the consumer. The consumer sells his labor and receives a salary for it, which he spends to pay for goods and services. The state also participates in market relations, while playing several important roles at once. It buys goods from resource markets, producers and intermediaries; pays them; collects taxes from these markets (including the consumer market); provides the necessary public services (provided by government agencies and public enterprises). Thus, the economy of each country and the economy of the whole world is a complex complex of markets that are interconnected by exchange processes. The market is perceived not only as a place where the seller and the buyer really meet. Thanks to modern means of communication and transportation, a trader can freely advertise his goods on TV in the evening, take orders from thousands of consumers by phone, send goods by mail the next day without making physical contact with customers. In business, the term "market" is used to refer to a group of consumers, united by some criterion. We can mention, in particular, the market of needs (one of such markets is created, for example, by consumers who care about their health and want to receive exceptionally high-quality goods); commodity markets (eg consumer electronics market); demographic markets (for example, adolescents or "baby boomers" - people born in the 1950s during the "baby boom" period, that is, a sharp increase in the birth rate in the United States); geographic markets (United States of America or Western Europe). This concept is used not only to refer to specific groups of consumers. For example, the labor market is made up of people who offer their labor in exchange for wages or goods. Various organizations, including employment agencies and recruitment consultants, emerge in the labor market to facilitate its functioning. Financial markets are of great importance because people have needs such as borrowing and lending, saving and saving their money. Modern marketingThe notion of markets finally brings us to a fuller definition of marketing. Marketing means the management of the market in order to carry out an exchange to meet the needs and demands of a person. So, we are back to our definition of marketing as a process in which individuals and groups of people get what they want and want through the creation of goods and consumer values and sharing them with each other. Exchange processes do not happen by themselves. Sellers must seek buyers, identify their needs, create quality products and services, promote, store and deliver them. Product development, market analysis, communication, distribution, pricing and service are the main types of marketing activities. We are used to thinking that marketing is mainly done by the selling side, but buyers, it turns out, take part in it - when they are looking for new products at affordable prices. Purchasing agents are also involved in marketing, looking for sellers with whom to make profitable deals. The seller's market assumes that the seller has more power and the buyer is a more active participant in the market. In the buyer's market, the buyer has more power and the seller must be an active participant in the market. The figure below shows the main elements of a modern marketing system. In a standard situation, marketing means serving the end-consumer market in a competitive environment. The company and its competitors send their products and information about them to end consumers - directly or through marketing intermediaries (intermediaries). All the actors in this system are influenced by the same environmental factors (demographic, economic, environmental, scientific and technical, political and legal, socio-cultural). We'll take a closer look at all the factors that influence marketing decision making.
Fig. The main actors and forces in the system of modern marketing Each of the components of the marketing system contributes to the creation of customer value. Thus, the success of a company depends not only on its own actions, but also on how well the needs of the end user are met by all links in the chain. IKEA would not have been able to provide buyers with the low prices it promised if the company's suppliers were selling them at exorbitant prices. And Toyota would not have been able to offer high-quality vehicles to consumers if its dealerships had not provided excellent customer service. (reklama) (reklama) (reklama) (reklama) (reklama) Marketing is a social science, so it affects a great many people. The main goals of marketing are as follows. 1. Maximizing the highest possible level of consumption - firms are trying to increase their sales, maximize profits using various methods and methods (they introduce fashion for their products, outline a sales growth strategy, etc.). 2. Maximization of customer satisfaction, that is, the purpose of marketing is to identify existing needs and offer the largest possible range of homogeneous goods. But since the level of customer satisfaction is very difficult to measure, it is difficult to evaluate marketing activities in this area. 3. Maximizing choice. This goal follows and, as it were, is a continuation of the previous one. The difficulty in realizing this goal is not to create an abundance of brands and imaginary choice on the market. And some consumers, with an excess of certain product categories, feel anxiety and confusion. 4. Maximizing the quality of life. Many are inclined to believe that the availability of an assortment of goods favorably affects its quality, quantity, availability, cost, that is, the goods are "improved", and therefore, the consumer can satisfy his needs as much as possible, improve the quality of life. Proponents of this view admit that improving the quality of life is a noble goal, but at the same time this quality is difficult to measure, therefore contradictions sometimes arise. Marketing tasks: 1) research, analysis, assessment of the needs of real and potential buyers; 2) marketing assistance in the development of a new product (service); 3) providing service maintenance; 4) marketing communications; 5) research, analysis, assessment and forecasting of the state of real and potential markets; 6) research of competitors' activities; 7) sales of goods (services); 8) the formation of an assortment policy; 9) formation and implementation of the company's pricing policy; 10) the formation of the strategy of the firm's behavior.
Similar pages found: 10 Company goals and objectives are incredibly valuable to your brand, and they can both strengthen and weaken the connection with potential and current customers. But understanding the meaning of these terms is not as easy as it seems. Often times, marketers think of goals and objectives as synonymous. But this is not the case. Brands need to be able to articulate goals and objectives that will lead them to success. Goals and Objectives: What's the Difference?In marketing, the terms “goals” and “objectives” are usually not delineated. But there is a difference between them. Understanding her can be the key to a brand's success.
First, the brand must articulate the goals or expected results of the marketing efforts. Then, focusing on the goals, it is necessary to draw up a list of actions and initiatives necessary for their implementation. Let's say you want to improve your website traffic and engagement metrics. In this case, your goals will be to increase traffic and visitor engagement. Specific strategies to achieve these goals, such as posting SEO content and promoting it on social media, are up to you. Take a SMART approachWhen setting goals, use a SMART approach, according to which they should be:
The following template will also help you formulate your goals: By ______ (time / date), the marketing team of ______ (company name) will reach ______ (number / metric) _____ (metric). You can also use the “every ______ (time span)” benchmark to formulate recurring goals for the team. From the above, it is clear that “getting more traffic to the site” is not a SMART goal. Here's how it should be phrased: “By the end of Q2 2018, JessWells Incorporated's marketing team will be attracting 1,200 visitors per month to the site.” So much better. When formulating goals, it is important to remember that they must be specific. Marketing teams often have the following goals:
Such formulations are ineffective. They should always be supplemented with specific metrics:
The more specific your goals are, the easier it is to formulate objectives. Setting goalsOnce you've set specific and measurable goals, your team can begin to formulate objectives. That being said, it's important to focus on data about your audience. For example, if you find that consumers are actively responding to email newsletters, this technique is definitely worth incorporating into your marketing strategy. Common mistakesThe following tests can help you avoid common mistakes:
SWOT analysisIf you find it difficult to define the goals and objectives of your marketing efforts, use the SWOT brainstorming technique. It involves analyzing internal and external factors and identifying the elements that set you apart from your competitors, as well as obstacles to success. SWOT stands for:
This approach will ensure that your goals and objectives align with your overall business goals. To do this, you need to consider the following points:
After answering these questions, it is important to bet on brand strengths and opportunities, while trying to minimize the impact of your weaknesses and external threats. type of promotion involving any non-personal paid form of product presentation monologue communication medium form of implementation of sales operations and methods of obtaining information about consumers + type of promotion, involving personal contact and interaction (dialogue) between the seller and the buyer 206. In the theory of marketing, the "electronic market" in the Internet environment is characterized by the following statements ... + 24/7 market availability Limited market availability + The global nature of the market Limited information for consumers 208. In the theory and practice of marketing, the following measures of government influence on marketing regulation are distinguished ... + Consumer protection legislation + Setting fixed prices for certain types of goods Centralized planning of production volumes by manufacturers 209. State control over prices for certain goods and services leads to the emergence of ____________ prices ... Retail Exchange + Regulated Market capacity determines. Proposed benefits from subsequent product sales Counted number of items sold + Possible volume of sales of goods The total cost of upfront costs 212. Before formulating the goals of the marketing of the company, it is necessary ... + Analyze the current situation of the company in the market. Develop a plan for each of the 4Ps Draw up a sales work plan 213. A characteristic feature of observation as a method of obtaining marketing information is ... Using artificial conditions for research Collection of direct information from secondary sources Active participation of the observer in the process under study + Passive event registration 216.The life cycle of the product "household appliances" is longer in ... Germany + Russia 217. The definition of marketing is inappropriate ... A management process aimed at identifying and meeting the needs of the consumer, with the aim of making a profit for the company The area of management, the functions of which are to ensure effective demand, to obtain a set profit, to promptly bring the product to the consumer + Management system for production and sales of goods The process of managing the needs of the population 218. In marketing practice, desk research is used for the following purposes ... Study of socio-cultural factors + Analysis of the dynamics of the economic environment Obtaining new data on the problem under study Collecting current information on consumer reactions to marketing mix events 219. In marketing theory, depending on the number of resellers, the following product distribution strategies are distinguished from those listed below ... Diversification + Exclusive sales + Selective marketing Specializations 220. Promotion of a product on the market is an element ... Personal sales Propaganda + Complex marketing 221. The “marketing environment” consists of…. needs and requirements of buyers + two components: "microenvironment" and "macroenvironment" collection of information, pricing policy, sales promotion economic agents that make up the environment of the firm
Maturity + Bringing goods to market 223. In marketing practice, the product concept is applied in the following cases ... The organization does not conduct consumer analysis The consumer is interested in the low price of the product + The consumer is interested in high quality goods + The organization researches the market and knows the needs of consumers 225. The Russian market of geoinformation technologies is segmented by territorial lines (global, national, regional, municipal). This segmentation feature is ... Socio-economic Demographic Psychographic + Geographic 226. The instrument for collecting primary information is not ... Monitoring customer behavior Supplier social survey Manipulation of the price of a product to study fluctuations in sales volumes + Market research data of a competitor 228. ZHTsT (product life cycle) represents…. A set of conditions necessary for a product to enter the market + The time interval from the introduction of the product to the market to the "dying of the product" The range of time from the first development to the moment of its implementation Phase sequence of production and implementation 229. In marketing practice, an organization can use the following media ... Vehicles, buildings, structures + Newspapers, magazines Statistical reports In-house reports 234. In marketing theory, the “growth” stage of life cycle cycle is characterized by the following features ... + rapidly growing sales volumes insignificant sales + intensive promotion conditions low price of goods 235. Legal entities and individuals who help a manufacturing enterprise to find consumers and (or) sell their products are called…. + Resellers Firms that carry out goods movement 236. The types of marketing research objectives are NOT ... Experimental Analytical + Justifying Descriptive 237. In the activities of the organization, marketing functions are aimed at ... + Organization and implementation of exchange between the organization and consumers Maximizing the profit of the organization + Formation and development of demand with constantly changing needs Maximizing product sales 239. When implementing the product concept, the term “marketing myopia” means ... Aggressive marketing efforts + Improving the product without taking into account the needs of consumers Refusal to release a new product Using only wholesale resellers 240. The law of supply, if prices rise, ceteris paribus, manifests itself in .... Slowdown in supply growth + Growth in supply Falling supply Reducing demand 241. From the point of view of marketing theory, the following factors influence consumer behavior in the market ... + Psychological Legal + Social Political 242. The release of a universal shampoo belongs to the ___________ marketing strategy ... .. Differentiated Concentrated Fundamental + Massive 243. In the theory of international marketing, economic factors that characterize the structure of the country's economy, the level of development of its individual sectors, determine ... + Income levels of different segments of the population Sustainable norms of behavior Customs and traditions of the population + The country's needs for goods and services 244. The complex of service maintenance as an element of goods reinforcement does not include ... Sales service + Market service Pre-sale service After-sales service 245. In marketing theory, modern communication processes are characterized by the following features ... + Standardization of communication tools + Diversity and integration of communications Unification of communications Use of differentiated marketing tools in communications 246. In marketing theory, planning principles include the following from the following…. + Efficiency + Adaptability Objectivity of assessment Variation 248. An approach to the organization of marketing, in which marketing acts as one of the functional areas of the organization, along with such functions as production, finance, personnel management, etc., is called ... An integrated Ideological + Functional Information 249. Marketing concept of the market…. Population of a given country Location of consumers with similar needs + A set of existing and potential consumers of the product Average sales volume over the past 5 years 250. Market supply- ... The willingness of a manufacturer to produce and sell a specific quantity of goods at a specific price in a specific period of time Manufacturer's target setting The willingness of the buyer to purchase a certain amount of goods in a specific period of time 252. An observation using a rigidly defined event registration scheme is called ... + Structured Personal Schematic 255. The advantages of a market structure of marketing management are ... Increasing the motivation of managers by region Thorough revision of business strategies in various segments Combining the advantages of different types of structures + Responsibility of employees for activities in each market 256. ZhTsT represents…. The period of time during which a product is in production, in the market and in consumption The period of time during which the product is in the sphere of consumption + The period of time during which the product is on the market The period of time during which the product is on the market and in the consumption area 259. The market segment is ... Market that specializes in a certain type of product Target market + A group of consumers formed according to certain criteria Market administrative unit 260. A PVC window company publishes a 10% discount coupon for a balcony window in the local newspaper, which is part of…. Propaganda Personal sales Sales promotion 264. The states of the southern and southwestern United States are experiencing an annual population increase of 12 million households, resulting in a steadily growing demand for air conditioners and other climate control devices. For an air conditioning company, this is ... Favorable controlled factor of the external environment Favorable controlled factor of the internal environment + Favorable uncontrolled environmental factor Favorable uncontrolled factor of the internal environment 267. The method of tender pricing refers to the group…. Parametric pricing method Demand-driven pricing method Costly pricing methods + Competitive pricing methods 269. One of the principles of marketing is ... Sales promotion + Taking into account the requirements of the consumer 272. In the theory of marketing, the following requirements are imposed on distribution channels from the following .... Profitability + Availability + Stability Sociability 274. Changing the assortment of goods by varying the goods means ... Creation of a complimentary (related) product New product creation Creating a new product to replace the old product variant + Creating a product with changing parameters along with the old product options 280. The need for their behavior when buying a cool drink "bread kvass" is guided by seasonal demand. In this case, it is advisable…. Remarketing Conversion Marketing Demarketing + Synchromarketing 287. In marketing theory, public marketing as a type of marketing activity is aimed at…. Increasing the proportion of target groups of the public + Changing the behavior of representatives of target groups of the public Increased income from social activities + Creation, formation and change of public opinion 290. When developing strategies for social change in social marketing with the initial stages are the following…. Implementation and control of execution Development of an organization plan Analysis of beliefs, attitudes, values and behavioral manifestations of a particular social stratum + Setting goals for social change 294. A well-known economist who made a significant contribution to the development of marketing ... F. Taylor + F. Kotler A. Fayol 295. When he sells something to firms that does not have a specific material form, he sells a promise to do something that has value for the client, then they mean marketing ... + Services Promises Politician 297. If the product of the firm has passive demand (for example, insurance of individuals), then the concept is appropriate ... + Intensification of commercial efforts Manufacturing improvements Product improvements Marketing 298. In marketing theory, the stage of the product life cycle "introduction to the market" is characterized by the following features ... + Insignificant sales volume High profit + High marketing costs Rapidly growing market share 300. The definition of a buyer's market in marketing is ... The demand far exceeds the supply, and the buyer plays the main role in the market. Supply is much higher than demand, and the seller plays the main role in the market Supply is much lower than demand, and the seller plays the main role in the market + Demand is much lower than supply, and the buyer plays the main role in the market 301. When a firm sells one type of product at one price, and advertising is directed to the entire market as a whole, then a market coverage strategy is used ____ marketing Fundamental Concentrated Differentiated + Undifferentiated 303. It is more a marketing slogan ... Everything that is produced must be bought "Get" a client and make him buy a product without delay + Produce only what will be bought Love the customer, not the product 304. Independent brokers in the marketing of products ... Do not buy goods at their own expense + Are not the owner of the goods they sell Work for a commission + Work as brokers or distributors 306. Field studies are studies for which ___ information is used + Specially assembled Received at random |
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
New
- Unlawful suspension from work
- Features of dismissing an employee without his desire according to the law
- Labor Code 180 Part 2
- Is a verbal order an order?
- About professional standards
- Twenty distinctive qualities of a leader
- How to find out the speed of your Internet connection What affects the speed of the Internet
- Blind typing: free keyboard trainers online
- Marketing analysis of the market: types, stages, methods
- Payment order and details for paying the trade fee